BIOLOGY & SEX
We got bodies! And we need to know how the hell they work!
Everyone’s body parts look a little different.
The size and shape of your exact biology may differ from these drawings, but the inner workings are all the same.
FEMALE ANATOMY DIAGRAMS
REMEMBER: Everyone’s body parts look a little different.
The size and shape of your exact biology may differ from these drawings, but the inner workings are all the same.
ANATOMY OF THE VULVA
ANATOMY OF THE CLITORIS WITH INTERIOR VIEW
CLITORIS FROM THE INSIDE
This drawing shows what the clitoris looks like inside your body that you can’t see from the outside. They are the parts of your clitoris that fill with blood when you are turned on.
ANATOMY OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
KEEP IT CLEAN + DON’T STINK
It’s important to wash your body with soap and water regularly. Make sure you wash between and around your labia.
DISCHARGE
Vaginal discharge is normal & varies during the menstrual cycle. Before ovulation (the release of the egg through the fallopian tube), there is a lot of discharge produced. It is usually white, transparent, thick or thin, & odorless. This is formed by normal bacteria and fluids from vaginal cells. During ovulation discharge is clear & stretchy, similar to egg whites. Panty liners can be helpful with discharge. If you experience any discharge that is yellow, green, clumpy like cottage cheese, or has a bad odor, see a doctor.
It’s the body you were born with.
Know how it works, so you can have the most fun with it.
MALE ANATOMY DIAGRAMS
REMEMBER: Everyone’s body parts look a little different.
The size and shape of your exact biology may differ from these drawings, but the inner workings are all the same.
ANATOMY OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
DISCHARGE
Pee and semen are the two fluids that will come out of a penis. If it hurts to pee or reach orgasm, see a doctor. If you experience any discharge that is yellow, green, clumpy like cottage cheese, or has a bad odor, see a doctor.
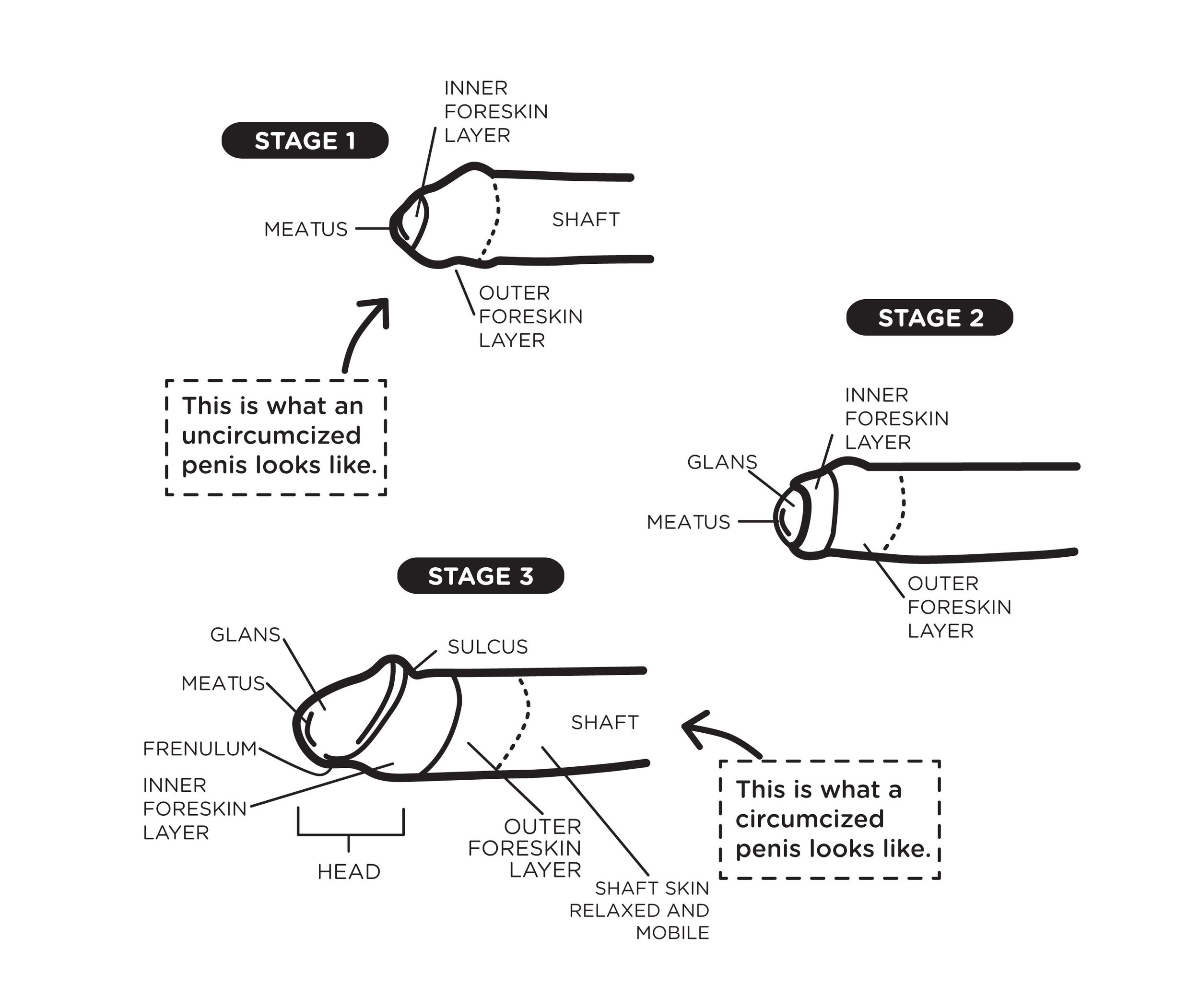
STAGES OF ERECTION
KEEP IT CLEAN + DON’T STINK
It’s important to wash your body with soap and water regularly. If you have foreskin, make sure you pull it back and wash under it and around the head of your penis.
SEXUAL ACTIVITY
It’s most important to only do what you are comfortable doing, only with people you are comfortable doing it with. Never let someone else pressure you into doing something you’re not ready to do.
THERE ARE MANY TYPES OF SEXUAL ACTIVITY
Kissing — on the mouth, with the tongue, on body parts
Massages — touching someone’s body in an erotic way
Touching — a partner’s nipples, breasts, or sex organs
Sex talk — sexting, phone sex, cybersex, “talking dirty” during sex
Rubbing — bodies together — with or without clothing
Watching — or reading pornography
Intercourse — both anal and vaginal
Oral sex — stimulating a partner’s sex organs with the mouth
Using sex toys — alone or with a partner
Masturbation — or mutual masturbation
MASTURBATION
Masturbation is touching one’s own body, including sex organs, for sexual pleasure. It is a normal, common, reliable, and safe way to get sexual pleasure. Masturbation has many health benefits, such as: improved sleep, reduced stress, relieves menstrual cramps, and provides sexual pleasure for people who practice abstinence. Masturbation is a natural and common activity for everyone.
FEMALES: May stimulate any part of their vulva, including the clitoris, inner or outer labia, the vaginal opening or canal, and/or the perineum or anus. Many women prefer rubbing near — but not on — the clitoris because direct stimulation can be very intense. Everyone has their own preferences.
MALES: May stimulate the penis, scrotum, perineum, and/or anus. Everyone has their own preferences.
EVERYONE:
May touch other sensitive areas of their bodies. There are nerve endings that can create “erogenous zones” all over the body. People may experience pleasure by touching places like the breasts, nipples, or thighs. They may also use sex toys like vibrators and dildos during masturbation.
May use lubricant or lotions to increase pleasure and protect against irritation.
Sex fantasies are normal and healthy. They may fantasize with their own thoughts or with erotic images or language — in print, on video, or online.
Knowing more about sexual anatomy helps in understanding masturbation. See sexual anatomy pages for detailed diagrams.
SEX ACTS
NOTE:
Shower and pee after sex to help avoid Urinary Tract Infections (UTI)
Sex acts may involve other forms of genital stimulation, such as solo or mutual masturbation, which may involve rubbing or penetration by the use of fingers, hands, or with a sex toy, such as a dildo or vibrator. There are numerous sex positions that participants may adopt in any of these types of sexual acts; the number of sex positions is essentially limitless.
INTERCOURSE DIAGRAM
Sexual intercourse is something people do for pleasure, and to make more humans.
Sexual intercourse between a penis and a vagina is how pregnancy occurs. Semen, with sperm in it, is ejaculated into the vaginal cavity. The sperm then swims up through the cervix to the fallopian tube, where the sperm may meet an egg.
There are other types of sexual intercourse, such as the below combinations, but they do not directly lead to pregnancy. Most sex that humans engage in is for plea- sure as opposed to procreation.
Remember, any time semen spills on the vulva, there is a possibility the sperm can swim up the vaginal canal and meet an egg and possibly fertilize it.
OVULATION & FERTILIZATION
Ovulation is the release of an egg from the ovaries. After ovulation, the egg will be available to be fertilized by sperm. In addition, the uterine lining (endometrium) is thickened to be able to receive a fertilized egg. If no conception occurs, the uterine lining as well as blood will be shed during menstruation.
In humans, ovulation occurs about midway through the menstrual cycle. The few days surrounding ovulation (from approximately days 10 to 18 of a 28-day cycle), constitute the most fertile phase. The time from the beginning of the last menstrual period (LMP) until ovulation is, on average, 14.6 days.
Ovulation rarely occurs exactly on the 14th day of your cycle. Stress, exercise, diet, and sleep can change your cycle month to month.
Cervical mucus changes when ovulation occurs. During the first few days after your menstrual cycle, the cervical mucus will be dry. As you approach ovulation, the cervical mucus will increase and become slippery, clear, and stretchy.
ALL ABOUT PERIODS
FIRST: LET’S END PERIOD SHAMING
Every human with a uterus in the history of humanity has had a period.
Each month, the uterus sheds its lining, sending blood flowing out through the vagina.
This process is as natural as eating, drinking and sleeping, and it’s beautiful too.
“There’s no human race without a period.”
– RUPIKAUR AND PRABH KAUR
THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
Usually runs about 21-35 days.
Our bodies are all different so cycles can range in length and still be considered normal.
PART ONE
The cycle begins on the first day of the period. The lining of the uterus and blood is shed out of the vagina (usually around 5 days +/-)
PART TWO
Bleeding has stopped, hormones stimulate the follicles to develop in the ovaries. Each follicle contains an egg. The lining of the uterus starts to thicken, waiting for a fertilized egg to implant there.
PART THREE
Around halfway through the cycle, hormones cause the follicle to burst and release an egg from the ovary. This is called ovulation. In the next few days the egg travels down the fallopian tube and attaches to the lining of the uterus. During this time, a sperm can fertilize the egg and cause pregnancy.
PART FOUR
If the egg is not fertilized, hormone levels will drop which signals the next period to begin. The egg will break apart and be shed out of the vaginal canal along with the lining of the uterus. If the egg does become fertilized, that is the beginning of pregnancy.
KEEP TRACK
Use a calendar, planner, or phone app to predict when your next period is coming or when you are ovulating (a.k.a.more likely to get pregnant). Your doctor will always ask you when your last period was.
PERIOD PROBLEMS:
Amenorrhea (ay-men-uh-REE-uh) The lack of a period Can be caused by pregnancy, extreme weight loss, eat- ing disorders, stress, and serious med- ical conditions. Talk to a doctor.
Dysmenorrhea (dis-men-uh-REE-uh) Painful periods, severe cramps
For some, heating pads or warm baths can help. Also taking over the counter pain medication (Advil, etc) can help. Talk to a doctor about what’s causing the problem to treat it.
PERIOD FACTS:
Stress, exercise, diet, & sleep can change your cycle from month to month.
Many have irregular periods, meaning they don’t happen the same time each month. The full cycle of a period can range from 21-35 days. This is consid- ered normal.
CONTRACEPTIVES / BIRTH CONTROL
When you use contraceptives during sex, it lowers the chance of catching diseases or getting pregnant.
THE KICKER: You have to actually use or do the contraceptive method in order for it to work.
They have varying degrees of effectiveness, mostly depending on user error.
Here are some of the types of contraceptives you can use to make having sex safe and fun:
NOTE: Practicing safe sex is a sexy way start sex play and intercourse!
ABSTINENCE
Not having any kind of sex play or intercourse with a partner.
DISADVANTAGES You do not have sex. People may find it difficult to completely abstain from sex. They may not be prepared with another form of birth control.
IMPLANT
A matchstick-sized rod containing estrogen and progestin hormone is inserted in the arm. **Not effective against STDs.
POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS: May decrease or increase heaviness of period or spotting, change in sex drive, nausea, pain at the insertion site, or weight gain.
PATCH
A small patch that sticks to your skin and releases estrogen and progestin hormones. **Not effective against STDs.
POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS: Similar to other hormone methods: may decrease or increase heaviness of period or spotting, change in sex drive, nausea, vomiting, change in sexual desire, or irritation on skin.
PILLS
Pills taken daily containing estrogen and progestin hormones. **Not effective against STDs.
POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS: Similar to other hormone methods: may decrease or increase heaviness of period or spotting, change in sex drive, nausea, vomiting, change in sexual desire, or irritation on skin.
HORMONE SHOT
A shot in the arm or butt containing estrogen and progestin hormones. **Not effective against STDs.
POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS: May decrease or increase heaviness of period or spotting, change in sex drive, nausea, pain at the insertion site, or weight gain.
SPONGE
Spermicide sponge covers the cervix and blocks sperm from entering the uterus.**Not effective against STDs.
DISADVANTAGES: Can be difficult to insert or remove, may be pushed out of place by some penis sizes or heavy thrusting.
POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS: May cause vaginal irritation from spermicide allergy and may make sex too messy or too dry.
VAGINAL RING
A small ring containing estrogen and progestin hormones is insert- ed into the vagina once a month. **Not effective against STDs.
POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS: Similar to other hormone methods: May decrease or increase heaviness of period or cause spot- ting, change in sex drive, nausea, vomiting, change in sexual desire, irritation on skin.
CERVICAL CAP
A Silicone cup with spermicide blocks sperm from entering the uterus. **Not effective against STDs.
DISADVANTAGES: Cannot be used during period, difficult to insert, may be pushed out of place by heavy thrusting.
POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS: Vaginal irritation from spermicide allergy and may feel pain or discomfort when using.
CONDOM
Latex or plastic sleeve worn on the penis. Prevents pregnancy and STIs. Can be used with vaginal, anal or oral sex. It is the most convenient type of contraceptive.
DISADVANTAGES:
You MUST use it correctly every time you use it, for the entire duration of the sex. Have condoms close by before you engage in sexual activity so you can remember to use them.
DENTAL DAM
A thin, square piece of latex that helps prevent the spread of STDs when placed over the vulva or anus during oral sex.
DISADVANTAGES: Specifically to be used for oral pleasure, not to be use as contraceptive.
DIAPHRAGM
A shallow silicone cup inserted into the vagina. Must be used with spermicide. **Not effective against STDs.
DISADVANTAGES: Cannot be used during period, difficult to insert, may be pushed out of place by some penis sizes or heavy thrusting.
POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS:
Vaginal irritation from spermicide allergy and may feel pain or discomfort when using.
FEMALE CONDOM
A pouch inserted into the vagina to prevent pregnancy by catching precum and semen. Reduces the risk of STIs.
DISADVANTAGES:
Most people have no problems but it can cause irritation of the vagina, vulva, penis or anus. It can slip into the vagina or anus during inter- course, and can reduce sensation during intercourse.
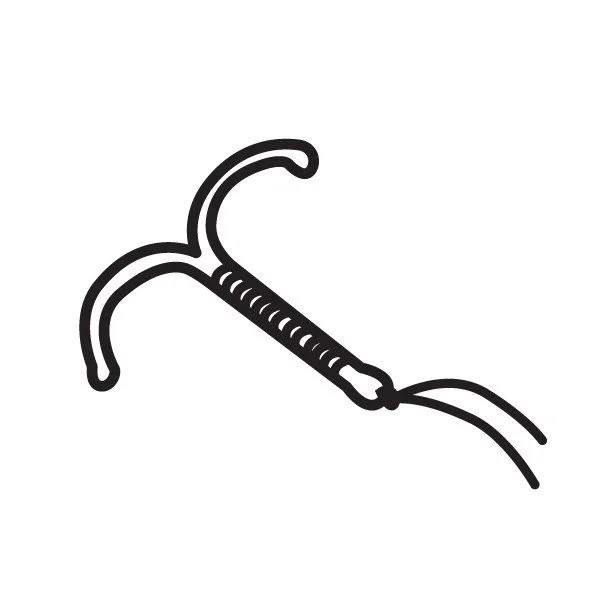
I.U.D
IUD or IntraUterine Device is a small contraceptive device that is put into the uterus (womb) to prevent pregnancy. It can be copper or plastic with hormones. IUDs change the way sperm move so they can’t get to the egg. **Not effective against STDs.
POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS: Mild to moderate cramping and back aches for a few days after IUD is inserted. May decrease or increase heaviness of periods or spotting.
MORNING AFTER PILL
Pills or Copper IUD to prevent pregnancy up to five days after unprotected sex. **Pills may not work as well depending on body mass index.
DISADVANTAGES: Must use up to 5 days (120 hours) after sex. If you’re already pregnant, the morning-after pill won’t affect your pregnancy. DO NOT use the morning after pill regularly. It is not as effective as other methods (IUD, or condoms).
SPERMICIDE
A substance that presents pregnancy by stopping sperm from moving. Use with other forms of birth control. **Not effective against STDs.
DISADVANTAGES: May not form a good barrier over the cervix and pregnancy can occur. Some people complain that spermicides are messy and may irritate the penis or vagina. Switching brands may solve the problem.
STERILIZATION
A surgery that prevents pregnancy permanently. The fallopian tubes are blocked. **Not effective against STDs.
DISADVANTAGES: This is permanent. You can never become pregnant again.
VASECTOMY
A surgery that prevents pregnancy permanently by blocking the tubes that carry sperm. **Not effective against STDs.
DISADVANTAGES: This is permanent. There are some reversal options but they involve expensive, complicated surgery. The reversal can have complications like pain, swelling, fever, and bruising.
PULL OUT METHOD
The act of pulling the penis out of the vagina before ejaculation.
**Not effective against STDs.
DISADVANTAGES: You must use the method correctly. Pregnancy can still occur with pre- cum or if semen is spilled on the vulva.
BREAST FEEDING
While breastfeeding, the body does not make a hormone that is necessary for ovulation.
**Not effective against STDs.
DISADVANTAGES: It’s not ONLY works, MAYBE for 6 months after giving birth, and even then, sometimes will not work. If formula is given to the baby, there’s a huge chance of getting pregnant again. Breastfeeding may reduce vaginal lubrication.
FERTILITY AWARENESS METHODS
FAMs, sometimes called the rhythm method, are ways to track ovulation in order to prevent pregnancy. Other preventative measures must be used like a condom on days when a woman is most fertile.
DISADVANTAGES: FAMs will not work if you are unable to abstain or use another method for at least 10 days during each cycle. It will not work as well if you have irregular periods, can’t keep careful records, are breast feeding, are a teenager, or using a hormonal birth control like the pill. It’s pretty much the worst way of preventing pregnancy.